EV Cars Battery Disposal: Safe Methods and Challenges
Electric vehicles are becoming the future of transportation, quieter roads, fewer emissions, and a major step toward cleaner air. But while EV technology is helping us move away from fossil fuels, it also brings up an important question: What happens to electric car batteries when they reach the end of their life?
EV battery disposal is a topic the world is still figuring out. These batteries contain valuable materials that can be reused, but they also hold harmful chemicals that can damage the environment if not handled properly.
In this blog, Drive UAE will break down the full lifecycle of EV batteries, the problems we face with disposal, and how recycling can help build a greener future for everyone.
What Happens When an EV Battery Wears Out?
Most EV batteries last 8–15 years, depending on driving habits, weather conditions, and the vehicle brand. However, they rarely stop working completely. Instead, the battery slowly loses its ability to hold a full charge, just like a smartphone battery over time.
When an EV battery drops below 70–80% of its original capacity, automakers consider it no longer suitable for powering a car. But that doesn’t mean it becomes useless. These batteries can take on a second life in other applications, such as:
- Home energy storage systems
- Solar and wind energy backup solutions
- Grid support for peak electricity loads
- Commercial power storage for businesses
So, disposal doesn’t happen immediately. The idea is to squeeze as much value as possible out of the battery first.
Why EV Battery Disposal Must Be Handled Carefully
EV batteries, especially lithium-ion types contain chemicals and metals like:
- Lithium
- Nickel
- Cobalt
- Manganese
- Electrolyte solutions
If disposed of incorrectly, these materials can:
- Leak into soil and water, causing pollution
- Trigger fires due to remaining electrical charge
- Harm wildlife and ecosystems
- Release toxic fumes when broken or burnt
This is why throwing EV batteries into regular waste is dangerous and illegal in many countries.
On the positive side, these metals are extremely valuable. Proper recycling allows the industry to recover them and reuse the materials in new batteries. That means less mining, less waste, and a more sustainable supply chain.
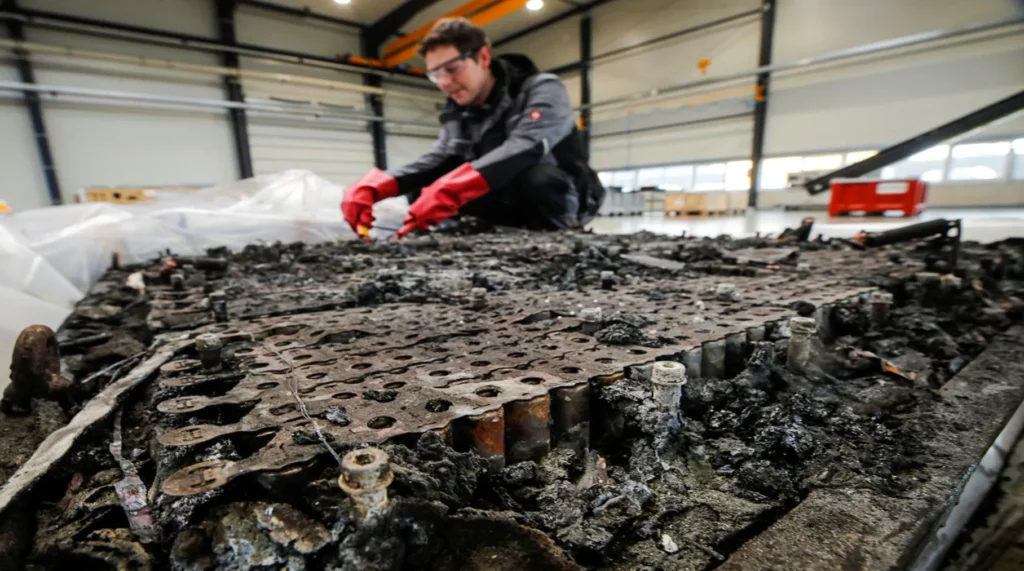

Challenges in EV Battery Disposal Today
Although recycling is beneficial, the world still faces significant hurdles:
Limited Recycling Infrastructure
Only a small number of specialized recycling facilities exist globally, and most are located in Europe, China, and North America. Many regions still rely on exporting used batteries abroad.
Complex and Expensive Processes
Recycling lithium-ion batteries requires:
- Advanced equipment
- Skilled workers
- Strict safety regulations
Not all recyclers are capable of handling large automotive batteries safely.
Transportation Safety Risks
EV batteries remain highly charged, even when old. Transporting them can be risky due to fire hazards and strict legal restrictions.
Lack of Standardization
Different automakers use different battery designs, making disassembly difficult. A universal battery design could make recycling far easier in the future.
As more EVs hit the roads worldwide, these challenges must be solved quickly to avoid a major waste crisis.
How EV Battery Recycling Actually Works
When a battery reaches the point where it can’t serve any useful purpose, specialized recycling facilities take over. The process typically includes:
Step 1: Collection and Safe Discharge
The battery is safely drained of electrical energy to prevent accidents.
Step 2: Dismantling
Technicians remove the casing, separate modules, and identify components that can be reused directly.
Step 3: Shredding
Materials are broken down into small pieces called “black mass,” containing precious metals.
Step 4: Material Extraction
There are three main approaches:
Pyrometallurgy
- High-temperature melting
- Fast and proven
- Energy-intensive
- wastes lithium
Hydrometallurgy
- Chemical solutions extract metals
- Higher recovery rate
- Requires chemical waste management
Direct Recycling
- Restores battery materials directly
- Most sustainable and cost-efficient
- Still in development phase
The goal is to return extracted metals back to battery manufacturers, creating a closed-loop system that reduces the need for new mining.
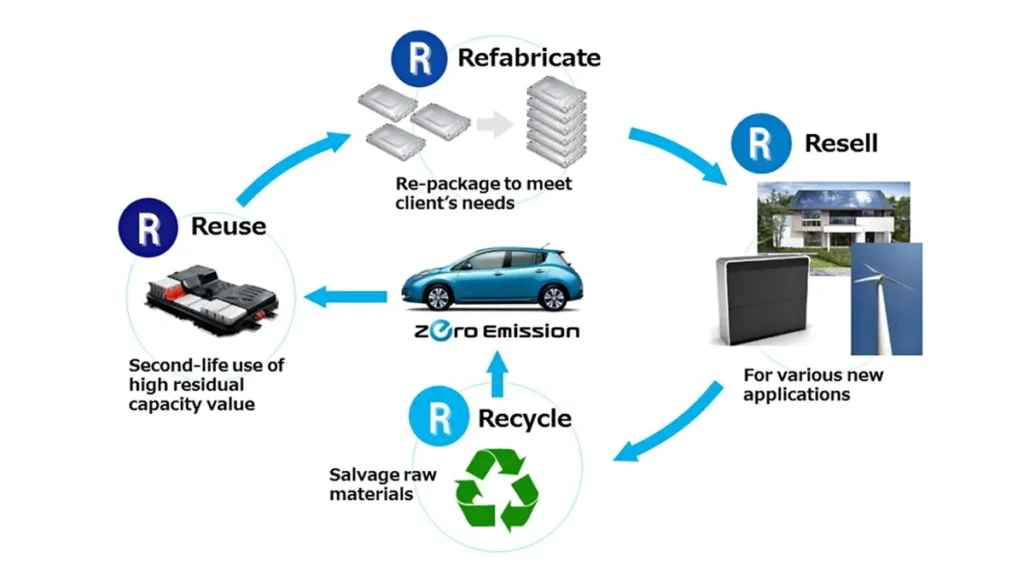
Second-Life Applications: Extending Battery Use Before Disposal
Before recycling becomes necessary, old EV batteries often get a second career in energy storage. Even with reduced capacity, they can store enough power to support:
- EV charging stations
- Home energy backup during outages
- Solar and wind farms
- Commercial building energy stabilization
This extra lifespan can add 5–10 more years of practical use, making the entire battery lifecycle far more efficient.
What Automakers and Governments Are Doing
Auto manufacturers recognize that responsible battery management is essential. Many brands already have recycling or take-back programs, including:
- Tesla’s in-house battery recycling
- Nissan using Leaf batteries for home storage systems
- BMW’s partnership for closed-loop recycling
- Hyundai and Renault repurposing used batteries for renewable storage projects
- Governments are also stepping in. For example:
- EU requires automakers to collect and recycle EV batteries
- China leads globally in recycled lithium material production
- Regulations are being developed in the UAE and GCC to support responsible EV waste handling
These efforts show that EV battery recycling is not optional, it’s becoming a legal and environmental necessity.
What EV Owners Should Do with End-of-Life Batteries
If your EV battery needs replacement, do not take it to a local scrap yard or landfill. Instead:
- Contact your vehicle manufacturer for guidance
- Visit an authorized EV service center
- Follow local environmental regulations
- Ask about second-life programs or recycling eligibility
Your responsibility doesn’t end at driving an electric car, proper disposal completes the sustainability cycle.
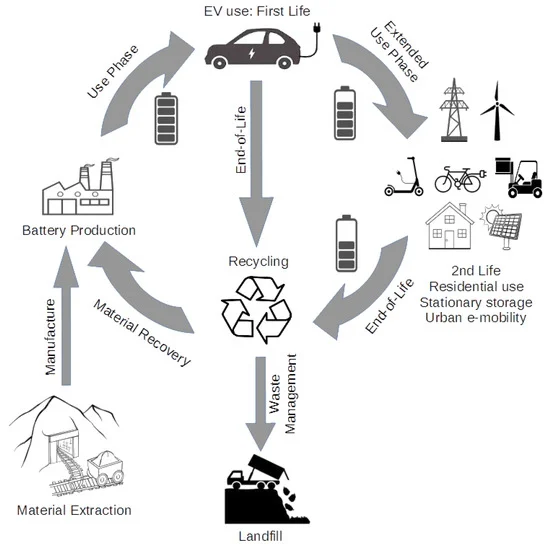
The Future: Toward a Zero-Waste Battery Lifecycle
The good news? The industry is evolving quickly. Scientists and engineers are working on:
- Batteries that use safer, more abundant materials
- Faster and more efficient recycling techniques
- AI-based battery management for longer life
- Universal battery designs for easier disassembly
- Larger recycling networks across all continents
In the future, the EV industry aims to achieve 100% recycling capability, meaning every battery can be reused or repurposed without harming the planet.
Final Thoughts
EVs are a big part of our move toward a cleaner environment. But to make them truly sustainable, we must handle their batteries responsibly from beginning to end. Recycling and second-life applications prevent harmful waste while conserving precious materials.
As more people switch to electric mobility, the world must expand recycling facilities, set global standards, and invest in safe, efficient disposal systems.
Choosing an electric vehicle is already a forward-thinking decision. Ensuring the battery is reused or recycled properly is an even greater contribution to a greener future.

