How to Check If a Car Is Imported & Why It Matters for Resale & Insurance
When buying a car in the UAE, it’s important to know whether it is locally sourced or imported. The UAE has a large market for imported vehicles, especially from Japan, the USA, Germany, and the UK. However, imported cars can come with different costs, registration requirements, resale values, and insurance implications.
Drive UAE will help you identify if a car is imported and explain why it matters for resale and insurance.
How to Identify an Imported Car in the UAE
Identifying an imported car isn’t rocket science. Here is how you can do it.
1. Checking the Vehicle History Report
One of the easiest ways to check if a car is imported is by obtaining a vehicle history report from:
- Emirates Vehicle Gate (EVG): Provides registration history and accident records.
- RTA (Roads and Transport Authority): Offers vehicle status reports in Dubai.
- Abu Dhabi Police Website: Useful for checking cars registered in Abu Dhabi.
A history report will show if a car was registered in another country before being brought to the UAE.

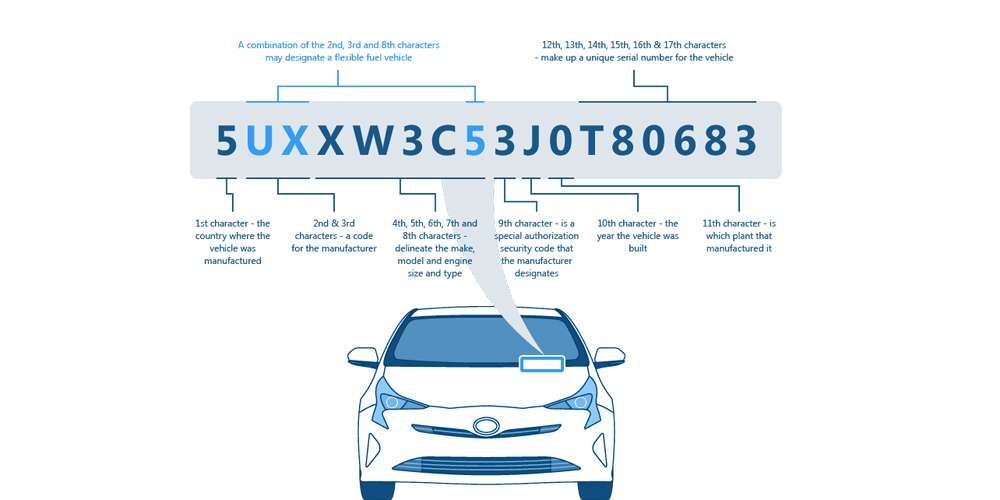
2. Verifying the Chassis Number (VIN Check)
Every car has a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) that can be used to trace its origin. You can check the VIN through the UAE Ministry of Interior Vehicle Inquiry Portal, CarFax (for US-imported cars), and AutoCheck (for global checks).
If the vehicle was first registered outside the UAE, it is an imported car.
3. Checking Registration and Number Plates
Locally registered cars in the UAE have plates issued by the RTA (Dubai), Abu Dhabi Police, or Sharjah Police. Imported vehicles may have temporary plates or foreign number plates before registration in the UAE. Some imported cars still have mileage in miles instead of kilometers, especially if they are from the US or UK.

Why an Imported Car Matters for Resale in the UAE
It matters because of the following reasons.
1. Depreciation & Market Demand
Imported cars often face higher depreciation due to:
- Lower buyer trust: Many buyers in the UAE prefer GCC-spec cars as they are built for local conditions.
- Limited resale options: Some imported models are harder to sell, especially if they lack Arabic-language navigation or local service support.
- Unknown accident history: US-imported cars may have a salvage or repaired title, reducing resale value.
GCC-spec vs. Imported Cars
GCC-spec cars are designed for extreme heat, sand, and humidity, making them more desirable. Imported cars (US, Japan, Europe) may have cooling system issues, different fuel requirements, or limited spare parts availability.

2. Popular Imported Car Trends in the UAE
- US imports: Common for luxury brands like Dodge, Ford, and Chevrolet but may have flood damage or accident history.
- Japanese imports: Toyota, Nissan, and Honda models are reliable, but right-hand drive conversions can affect resale.
- European imports: Mercedes-Benz and BMW are popular but may have different specifications from GCC models.

3. Resale Value Comparison
Here is a short comparison.
| Car Type | Resale Value | Buyer Demand | Maintenance Cost |
| GCC-spec car | High | Strong | Lower |
| US-imported car | Moderate | Moderate | Higher |
| Japanese Import | Moderate | High (Certain Models) | Moderate |
| European import | Low (Non-GCC) | Low | High |
Insurance Considerations for Imported Cars in the UAE
Here is what you need to know.
1. Higher Insurance Premiums
Insuring an imported car is usually more expensive due to:
Unknown history: Insurance companies charge higher premiums for imported cars with an accident or flood damage history.
Different safety standards: Non-GCC models may lack the safety features required for UAE regulations.
Expensive repairs: Imported cars may require special spare parts that are not locally available.
2. Insurance Policy Differences
Below are the insurance policy differences.
| Insurance Type | Best for | Coverage |
| Comprehensive Insurance | High-value imported cars | Covers theft, accidents, and third-party damage |
| Third-Party Insurance | Budget-friendly option | Covers damage to others, not your car |
| Extended Coverage | Luxury imports | Includes roadside assistance, off-road cover |
3. Best UAE Insurance Providers for Imported Cars
Some UAE insurers specialize in covering imported vehicles. Options include:
- GIG Gulf
- Oman Insurance (Now Sukoon Insurance)
- RSA Insurance
- Salama Insurance
Compare quotes before purchasing a policy to ensure the best coverage.
Regulatory & Registration Differences for Imported Cars
Below is a detailed description.
1. Import Taxes & Duties
When bringing an imported car to the UAE, the following fees apply:
- Customs Duty: 5% of the car’s value.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): 5% additional tax.
- Registration Fee: Varies by emirate (RTA Dubai, Abu Dhabi Police, etc.).

2. Registration Process for Imported Cars
To register an imported car in the UAE, you must obtain insurance, pass an inspection, and pay fees. You can apply for registration online or in person at the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA).
- Provide required documents to the customs authority at the port of entry
- Pay import duties, VAT, and customs fees
- Obtain a clearance certificate
- Get the vehicle inspected at an authorized testing center
- If the car is not GCC-spec, it must undergo modifications and an RTA inspection
- Get vehicle insurance from an authorized insurer
- Many insurance companies will cover all imported vehicles
- Apply for car registration through the RTA website or in person at the RTA
- Provide required documents, including, proof of purchase, completed application form, insurance documents, export plate number, customs clearance documents, vehicle inspection clearance, proof of residence, and pay registration fees.
- Collect the vehicle ownership card (Mulkiya), plate numbers, and the expiry date sticker.

Conclusion
Before buying a car in the UAE, checking whether it is imported or GCC-spec is crucial. To verify a car’s import status, check vehicle history reports chassis numbers, and registration details through UAE government portals.
If you plan to buy an imported car, ensure it is fully inspected, legally registered, and insured properly to avoid unexpected costs.

